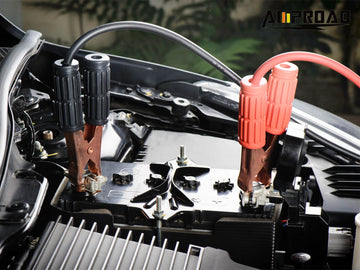
Jump starters are essential tools for reviving dead car batteries, providing a quick and efficient solution to get vehicles back on the road. When a car battery loses its charge due to factors like extreme weather conditions or prolonged periods of inactivity, a jump starter serves as a portable power source to jump-start the vehicle and restore battery function.
Voltage plays a crucial role in jump starting, as it determines the power output delivered to the dead battery. A jump starter typically provides a higher voltage than the car's battery, delivering a surge of electricity to kick-start the engine. This surge of power energizes the dead battery, allowing it to regain enough charge to start the vehicle.
By understanding the purpose of jump starters and the significance of voltage in jump starting, drivers can be better prepared to handle unexpected battery failures and ensure a smooth and efficient recovery process. Jump starters provide a reliable solution for overcoming dead batteries, offering peace of mind and convenience for drivers facing emergency situations on the road.
Voltage Requirements for Jump Starters
Standard Voltage for Vehicle Electrical Systems
Most car electrical systems operate on a 12-volt DC (Direct Current) standard. This means that the electrical components in a vehicle, including the battery, alternator, and various accessories, are designed to operate within a 12-volt system. Understanding this standard voltage is essential when considering the compatibility of jump starters with different vehicles.
Ideal Voltage Output for Jump Starters
Jump starters require a voltage slightly higher than that of a car battery to effectively overcome resistance and start the engine. While a fully charged car battery typically measures around 12.6 volts, jump starters typically provide an output voltage within a range of 12 to 16.8 volts. For example, the AMPROAD portable jump starter offers a starting voltage of 12 volts and a DC output range of 12 to 16.8 volts. This higher voltage surge from the jump starter delivers the necessary power to the dead battery, allowing it to regain enough charge to start the vehicle.
Understanding Voltage Compatibility
When selecting a jump starter, it's crucial to ensure that its voltage output is compatible with the electrical system of your vehicle. Using a jump starter with a voltage output that is too low may not provide sufficient power to start the engine, while using one with excessively high voltage could potentially damage the vehicle's electrical components.
Factors Influencing Voltage Output
Several factors can influence the voltage output of a jump starter, including its battery capacity, design, and overall quality. High-quality jump starters often feature advanced technologies and safety mechanisms to regulate voltage output and protect both the vehicle and the jump starter from damage during the jump-starting process.
Checking Voltage Output
Before attempting to jump-start a vehicle, it's essential to verify the voltage output of the jump starter to ensure compatibility. Most jump starters come with built-in indicators or displays that provide information about the voltage output and battery status. Additionally, consulting the vehicle's owner's manual can help determine the appropriate voltage requirements for jump-starting.
Maintaining Proper Voltage Levels
Proper maintenance of jump starters is crucial to ensure consistent and reliable performance. Regularly charging the jump starter according to the manufacturer's instructions helps maintain optimal voltage levels and prolongs the lifespan of the device. Additionally, storing the booster batterie in a cool, dry place when not in use can help prevent voltage fluctuations and preserve its effectiveness for emergency situations.
Understanding the voltage requirements for jump starters is essential for effectively reviving dead car batteries and getting vehicles back on the road. With most car electrical systems operating on a 12-volt standard, jump starters need to provide a slightly higher voltage surge to overcome resistance and start the engine. By selecting a jump starter with the appropriate voltage output and maintaining proper maintenance practices, drivers can ensure reliable performance and peace of mind when faced with unexpected battery failures.
Additional Considerations Beyond Voltage

Cranking Amps
In addition to voltage, another crucial factor to consider when selecting a jump starter is Cranking Amps (CA). Cranking Amps indicate the amount of current a jump starter can deliver to crank the engine and start the vehicle. While voltage provides the initial surge of power to kick-start the engine, Cranking Amps determine the strength and effectiveness of that initial burst of energy.
Higher Cranking Amp ratings are generally better for starting larger engines or vehicles with very dead batteries. The greater the Cranking Amps, the more power the jump starter can deliver to the engine, which is particularly important when dealing with stubborn or severely depleted batteries. When selecting a jump starter, it's essential to match the Cranking Amp rating to the requirements of your vehicle to ensure reliable starting performance.
How to Boost a Car: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we've covered the essential factors to consider when selecting a jump starter, let's discuss how to boost a car and revive a dead battery.
Prepare the Vehicles: Park the booster vehicle (with the charged battery) close enough to the dead vehicle so that the jumper cables can reach both batteries without stretching.
- Turn Off Ignitions: Ensure that both vehicles are turned off, including all electrical components such as headlights, radio, and air conditioning, to prevent any electrical surges during the jump-starting process.
- Connect the Jumper Cables: Connect one end of the positive (red) jumper cable to the positive terminal of the dead battery. Then, connect the other end of the positive jumper cable to the positive terminal of the booster vehicle's battery. Next, connect one end of the negative (black) jumper cable to the negative terminal of the booster vehicle's battery. Finally, connect the other end of the negative jumper cable to an unpainted metal surface on the engine block or chassis of the dead vehicle. Avoid connecting it directly to the negative terminal of the dead battery to reduce the risk of sparks.
- Start the Booster Vehicle: Start the booster vehicle and let it run for a few minutes to allow the dead battery to charge slightly.
- Attempt to Start the Dead Vehicle: Once the booster vehicle has run for a few minutes, attempt to start the dead vehicle. If it doesn't start immediately, wait a few more minutes and try again.
- Remove the Jumper Cables: Once the dead vehicle has started successfully, carefully remove the jumper cables in the reverse order of how they were connected, starting with the negative cable from the engine block or chassis of the dead vehicle, then the negative cable from the booster vehicle's battery, followed by the positive cable from the booster vehicle's battery, and finally the positive cable from the dead battery.
- Let the Engine Run: Allow the engine of the revived vehicle to run for a while to recharge the battery fully.
By following these steps and considering factors like voltage and Cranking Amps when selecting a battery booster, you can effectively boost a car and get back on the road in no time. Jump starters provide a reliable solution for overcoming dead batteries and ensure peace of mind for drivers facing unexpected roadside emergencies.
Essentials for Jump Starter Selection

Voltage and Cranking Amps: Key Considerations
In conclusion, when it comes to jump-starting a dead battery, understanding the key factors of voltage and Cranking Amps is essential for selecting the right jump starter and ensuring successful engine ignition.
Voltage Requirements
While most cars operate on a standard 12-volt electrical system, jump starters typically require a slightly higher voltage output, ranging from around 12.6 to 14.8 volts, to effectively jump-start a dead battery. This surge of power provides the necessary boost to overcome resistance and initiate the engine's ignition process.
Importance of Cranking Amps
However, voltage alone is not the only consideration. Cranking Amps also play a significant role in jump starter effectiveness. Cranking Amps indicate the amount of current a jump starter can deliver to crank the engine, and higher Cranking Amp ratings are generally better for starting larger engines or vehicles with severely depleted batteries.
Selecting the Right Jump Starter
By considering both voltage and Cranking Amps when selecting a jump starter, drivers can ensure compatibility with their vehicle's electrical system and optimize performance when faced with unexpected battery failures.
Ensuring Reliability
Investing in a high-quality jump starter that meets these specifications provides peace of mind and reliability during roadside emergencies, ensuring a quick and efficient solution to get back on the road safely.
FAQs / People Also Ask
Q1: What voltage does a vehicle jump starter need?
A: Vehicle jump starters typically require a slightly higher voltage output than the standard 12-volt electrical system found in most cars. Generally, jump starters need an output voltage ranging from around 12.6 to 14.8 volts to effectively jump-start a dead battery.
Q2: Why does a jump starter need higher voltage than the car's electrical system?
A: The higher voltage output from a jump starter provides the necessary power surge to overcome resistance and initiate the engine's ignition process. While most cars operate on a 12-volt standard, the additional voltage from the jump starter is essential for jump-starting a dead battery successfully.
Q3: What happens if the voltage output of the jump starter is too low?
A: If the voltage output of the jump starter is too low, it may not provide sufficient power to start the engine, leading to unsuccessful jump-start attempts. It's crucial to ensure that the jump starter's voltage output is compatible with the vehicle's electrical system to avoid potential issues.
Q4: Can a jump starter with excessively high voltage damage the vehicle's electrical components?
A: Yes, using a jump starter with excessively high voltage could potentially damage the vehicle's electrical components. It's essential to select a jump starter with an output voltage within the appropriate range to prevent damage to both the vehicle and the jump starter.
Q5: How do I determine the voltage requirements for my vehicle's jump starter?
A: To determine the voltage requirements for your vehicle's jump starter, consult the owner's manual or specifications provided by the manufacturer. Most jump starters come with built-in indicators or displays that provide information about the voltage output, making it easy to verify compatibility with your vehicle's electrical system.
Q6: Are there any safety precautions to consider when using a jump starter with higher voltage output?
A: When using a jump starter with higher voltage output, it's essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully and avoid prolonged exposure to the vehicle's electrical system. Additionally, ensure that all connections are secure and properly insulated to prevent electrical hazards during the jump-starting process.
Q7: Can I use a jump starter with variable voltage output?
A: Yes, some jump starters offer variable voltage output, allowing users to adjust the voltage based on the specific requirements of their vehicle. However, it's crucial to use caution and ensure that the selected voltage setting is compatible with the vehicle's electrical system to avoid damage.


